When we talk about networking, the concept of transferring information or data over a network usually comes in our mind. This happens with the help of the signals. These signals are used to carry information from one device to another efficiently.
There are 2 types of signals:
- Analog Signals
- Digital Signals
Analog signals
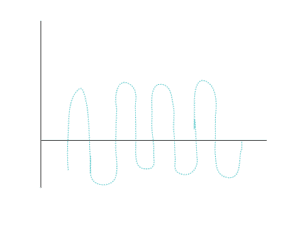
The analog signals can be described as the continuous waves. These continuous waves changes with respect to the time. The analog signals are represented by the sinusoidal waves.
Digital signals
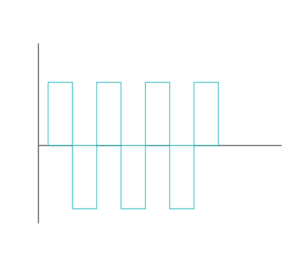
The digital signals can be described as discrete waves. These discrete waves have only two phases, that is, 0 or 1. The digital signals are represented by the square waves.
Difference between Analog and Digital Signals are given below:
| Basis | Analog signals | Digital signals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It can be defined as the continuous wave that always changes with respect to time | It can be defined as the discrete wave that always has a binary nature |
| Bandwidth | Low | High |
| Representation | The sinusoidal wave correctly represents the nature of an analog signal | Square wave correctly represents the essence of the digital signal |
| Signal Distortion | When noise occurs due to amplifier during transmission, there are more chances to have distortion | Low chances of having distortion during transmission |
| Technical aspect | Frequency, Amplitude, time period and phase completely describes technical aspect | The Bit intervals (period) and Bit rate (instead frequency) are used to describe the technical aspect |
| Signal Range | They do not have any kind of fixed range | Fixed and finite range, which are 0 and 1 specifically |
| Data Transmission | Transmit the data in the form of waves | Required to convert the transmitted data in the binary form, namely 0s and 1s |
| Example | The most suitable example for the analog signals could be the natural sound in our surroundings | The most suitable example for the digital signals could be Mobile phones and other electronic devices |
| Security | Less secure | Highly secure as it can be encrypted |
| Cost | Low | High, required device for conversion |
Key Differences
GENERIC
An analog signal can be defined as the continuous wave that always changes with respect to time; whereas; The digital signal can be defined as the discrete wave that always has a binary nature (0 or 1).
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION
The sinusoidal wave correctly represents the nature of an analog signal; whereas; The square wave correctly represents the essence of the digital signal.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
Frequency, Amplitude, Phase and Period completely describes the nature as well as the technical aspect of the analog signal; whereas; The Bit intervals, Bit rate, etc. efficiently describes the technical aspect as well as the nature of digital signals.
SIGNAL RANGE
When it comes to signal range for the analog signals then, they do not have any kind of fixed range; whereas; When it comes to the signal range for the digital signals then, they have fixed and finite numbers, which are 0 and 1 specifically.
SIGNAL DISTORTION
For analog signals the concept of signal distortion is directly proportional to the nature of the signal, that is, the analog signals are usually more prone to distortion; whereas; For the digital signals the concept of signals distortion is also directly related to the nature of the signal, that is, the digital signals are mostly less prone to distortion.
DATA TRANSMISSION
The data transmission is one of the most important factors for the signals; the analog signals always transmit the data in the form of waves; whereas; the digital signals always transmit the data in the binary form, namely 0s and 1s.
EXAMPLE
The most suitable example for the analog signals could be the human voice; whereas; the most suitable example for the digital signals could be the transmission in a computer.