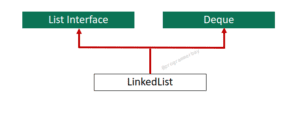
LinkedList is a child class of List and Queue interface. It owns the behaviour of Doubly Linked List and represents it as its underlying data structure . It is ideal to use when insertion or deletion are the frequent operations. In Linked List, elements are not stored in sequential manner,instead, each element in a Linked List is stored as a separate node, pointing to the previous and next elements in the list. The problem with linked list is, its performance degrades when it comes to retrieve operation or fetching an element.
Point to Remember:
1. It preserves insertion order and duplicates are allowed.
2. It accepts different types of objects and null insertions.
3. Similar to ArrayList, it is growable in nature, meaning, its size can shrink or grow dynamically.
4. It is best choice when insertion and deletion operations are involved mostly.
5. It resembles doubly linked list data structure which provides flexibility to implement other algorithms and data structure such as Stack,Queue and more.
6. It has the worst performance in case of fetching or accessing an element from the list as it provides linear-time performance.
7. It implements Serializable and Clonable interface but not RandomAccess interface.
8. It is not thread-safe, which means that multiple threads cannot safely access and modify the list at the same time.
9. It becomes slower than other List implementations when it comes to traversing over elements.
Method of Linked List Class
Linked List implements List and Deque interface. Therefore, there are several methods implemented by this class.
Below are the methods inherited from Deque.
| Method | Explanation |
|---|---|
| addFirst(element) | It adds the given element at first position in the given list |
| addLast(element) | It adds the given element at the end in the given list |
| element() | It returns head of the given list |
| getFirst() | It returns first elements of a linked list |
| getLast() | It returns last elements of a linked list |
| offer(element) | It adds the given element at the end of the list |
| offerFirst(element) | It adds element at the beginning of a list |
| offerLast(element) | It adds element at the end of a list |
| peek() | It returns head or first element of the given list |
| peekFirst() | It returns first element, if the list is empty, returns null |
| peekLast() | It returns last element, if the list is empty, returns null |
| poll() | It removes and returns first element of the given list |
| pollFirst() | It removes and returns first element, if the list is empty, returns null |
| pollLast() | It removes and returns last element, if the list is empty, returns null |
| pop() | It pops an element from the list, acting as Stack |
| push(E e) | It pushes an element from the list, acting as Stack |
| remove() | It returns and remove the head of a linked list |
| removeFirst() | It removes and returns first element |
| removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) | It removes first occurrences of the given element |
| removeLast() | It removes and returns last element |
| removeLastOccurrence(Object o) | It removes last occurrences of the given element |
Below are the methods is from List interface.
| Methods | Explanation |
|---|---|
| add(T obj) | It inserts an element to the end and returns true if it's added successfully |
| add(int indx, T obj) | It inserts the given element at the specified index of the list |
| addAll(Collection c) | It adds entire compatible collection objects to the end of the list |
| addAll(int indx, Collection c) | It inserts all the compatiable collection objects at the given index in the list |
| clear() | It removes or truncates all the elements from the given list |
| contains(Object obj) | It returns true if the given object is present within the list |
| containsAll(Collection obj) | It returns true if all the elements in the given collection are present in the list |
| equals(Object obj) | It returns true if the given object is equivalent to the list |
| hashCode() | It returns hashcode of a list |
| indexOf(Object c) | It returns the index of the given object which matches first, oterwise -1 is returned |
| isEmpty() | It checks whether a list contains any element or not. |
| iterator() | It returns iterator object for a list |
| lastIndexOf(Object obj) | It returns index of the given object which match first from the last, otherwise, -1 is returned |
| listIterator() | It returns object of ListIterator |
| listIterator(int indx) | It returns listIterator object with the starting point specified with indx. |
| remove(int index) | It removes an element from the specified position and returns the removed object from the list |
| remove(Object obj) | It removes very first occurrence of the given object from the list. |
| removeAll(Collection obj) | It removes all the elements that are present in the given collection from the list |
| replaceAll(UnaryOperator operator) | It replaces all the elements by performing the given operator to them in the list |
| retainAll(Collection c) | It retains all the elements that matches in the given list and removes all others from the list |
| set(int indx, T obj) | It replaces the given object at specified position and returns the replaced object. |
| size() | It returns number of elements present in the list |
| sort(Comparator c) | It sorts the list based on given order specified in the comparator. |
| spliIterator() | It returns SplitIterator object |
| subList(int from, int to) | It returns sublist that falls between fromIndx and toIndex |
| toArray() | t converts and returns an array corresponding to the given list |
Constructors of Linked List
There are two constructor present in Linked list class. These constructors are explained below :-
1) new LinkeList()
It is a default constructor that creates an empty linked list. Unlike ArrayList, it doesn’t have capacity issue.
Syntax:
LinkedList<T> l = new LinkeList<>() :
2) new LinkedList(Collection obj)
It creates a linked list instance, consisting elements of the given collection object.
LinkedList l = new LinkedList(Collection obJ);
Operations in LinkedList Class
1) Add an element
There are several methods provided by LinkedList class to add an element, such as add(), addFirst(),addList(),push(),offerFirst() and more.
Among all, add() and addAll() methods are most commonly used methods to perform add operation.
Program:
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> linkedList = new ArrayList<>(); // creating instance of linked list
// Adding elements to linked list
linkedList.add("Programmerbay");
linkedList.add("Example");
// Displaying elements of the list
System.out.println(linkedList);
// addAll method to add list of elements
linkedList.addAll(Arrays.asList("element1","element2"));
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}Output:
[Programmerbay, Example] [Programmerbay, Example, element1, element2]
2) Replace an element
LinkedList supports index based access which provides it the capability to update or replace an element at given position .
set() method is used for the purpose. Below is the code example.
Program:
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> linkedList = new ArrayList<>(); // creating instance of linked list
// Adding elements to linked list
linkedList.add("Programmerbay");
linkedList.add("Example");
// Displaying elements of the list
System.out.println(linkedList);
// set method to replace an element with new one
linkedList.set(1,"Removed") ; // Example would be replaced with Removed
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}Output:
[Programmerbay, Example] [Programmerbay, Removed]
3) Remove an element
Like several add() methods, LinkedList supports several methods to remove an element from a list i.e remove(),removeFirst(),removeLast() , pop() and more. The most commonly used methods are remove() and removeAll(). Below is a code example
Program:
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> linkedList = new ArrayList<>(); // creating instance of linked list
// Adding elements to linked list
linkedList.add("Programmerbay");
linkedList.add("Example");
linkedList.add("Test");
// Displaying elements of the list
System.out.println(linkedList);
// remove(element) method to remove the given element
linkedList.remove("Test"); // element Test would be removed
System.out.println(linkedList);
// remove(index) method to remove element from the given index
linkedList.remove(1); // element would be removed, sitting at 1st index which is example in this case
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}Output:
[Programmerbay, Example, Test] [Programmerbay, Example] [Programmerbay]
4) Traverse or iterate over elements
Like other implementation classes of List interface, elements of a linked list can also be traversed through various ways, iterator object and forEach are some of them.
With the help of iterator, we can traverse through all the elements in the given linked list. Also, enhanced for loop can also be used to loop through elements. Below are the code example.
Program:
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> linkedList = new ArrayList<>(); // creating instance of linked list
// Adding elements to linked list
linkedList.add("Programmerbay");
linkedList.add("Example");
linkedList.add("Test");
// traversing element using iterator object
System.out.println("Traversing using iterator :: ");
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// traversing element using for each method
System.out.println("Traversing using for each :: ");
for (String str:
linkedList) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}Output:
Traversing using iterator :: Programmerbay Example Test Traversing using for each :: Programmerbay Example Test
5) Converting List to Array
toArray() method provides the capability to convert a given linked list to array of objects. Below is the code example.
Program:
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> linkedList = new ArrayList<>(); // creating instance of linked list
linkedList.add("Programmerbay");
System.out.println("List view :: "+ linkedList);
Object[] array = linkedList.toArray();
System.out.println("Array view :: ");
for (Object obj:
array) {
System.out.print(obj);
}
}
}Output:
List view :: [Programmerbay] Array view :: Programmerbay