NavigableSet is a child interface of SortedSet that provides navigation methods to navigate through a set. It showcases the same behaviour as SortedSet with some additional navigable attributes & behaviour. It provides several methods that are only applicable to the implementation classes of NavigrableSet interface such as lower(), floor(), and ceiling methods to get elements less than or equal, greater than or equal and greater than a given element.
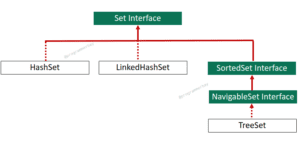
TreeSet and ConncurrentSkipListSet are two implementation classes of the interface.
Syntax:
NavigableSet<T> navigableSet = new TreeSet<>();
How to create object of NavigabelSet ?
Navigable Set is an interface, in order to create an object of that type, it is compulsory to have a implementation class of the respective interface. In this case, TreeSet can be used to create instance that can be assigned to NavigableSet type.
program:
public class SetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NavigableSet<String> navigableSet = new TreeSet<>();
// Adding elements to navigableSet set object
navigableSet.add("Example");
navigableSet.add("Code");
navigableSet.add("A");
// Displaying the output
System.out.println(navigableSet);
}
}Output:
[A, Code, Example]
It also allows a set to traverse in both orders, either ascending using an iterator or descending order with the method descendingSet(). Considering performance-wise, traversing elements in ascending order is faster than the traversing descending order. There are some more additional methods namely pollFirst() and pollLast() to remove the first and last element (lowest and highest element) from the set and return it.
Methods of NavigableSet Interface
Below are the methods that is offered by NavigableSet interface
| Methods | Explanation |
|---|---|
| lower(element) | It returns greatest element that is lower than the given element |
| higher(element) | It returns lowest element that is higher than the given element |
| floor(element) | It returns greatest element that is lower than or equal to the given element |
| ceiling(element) | It returns lowest element that is higher than or equal the given element |
| pollFirst() | It returns and removes first element from the set |
| pollLast() | It returns and removes last element from the set |
| descendingSet() | It returns reverse view of the given set. |
Below are the methods that is inherited from SortedSet.
| Method Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| comparator() | Returns comparator object which is used to define custom sorting order on elements in the set or returns null if the set is using some natural order |
| subSet(T from, T to) | It returns all the elements rangin from element "fromEle" to "toEle". If both the elements are same, then it would return empty set. It can throw IllegalArgumentException if the provided elements are not in range of the given set |
| headSet(elementObj) | It returns all the elements lesser than the provided element. It can throw IllegalArgumentException if the provided elements are not in range of the given set |
| tailSet(elementObj) | It returns all the elements greater than the provided element. It can throw IllegalArgumentException if the provided elements are not in range of the given set |
| first() | It returns very first element from the given set |
| last() | It returns last element from the given set |
Below are the methods that is inherited Set.
| Method Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| add(Object) | The method adds an element in a given set, returns false if one tries to add duplicate element |
| addAll(CollectionObj) | It adds all the elements of the given collection in a given set |
| clear() | It removes all elements from the given set |
| contains(Object) | It checks whether the given object consists in a set or not, if it returns true if exist, otherwise false |
| containsAll(CollectionObj) | It returns true, if all the elements of the given collection exist in the set, otherwise false |
| isEmpty() | It checks whether a set is empty or not. it returns if empty, other false |
| iterator() | It provides iterator object to iterate through set |
| remove(Object) | It removes the given object from the set, if present |
| retainAll(CollectionObj) | It retains elements of the collection provided in the method, and removed all other elements in the set that don't match the elements of collection object |
| size() | It returns number of elements present in a set |
| spliterator() | it returns spliterator object to iterate through set |
| toArray() | It converts given set and returns array |
| removeAll(CollectionObj) | It removes all the elements consisting in the collection object |