In this article, we’ll be going to discuss simplification concept, tricks and related questions that are often asked in quantitative aptitude test.
Concept:
Simplification mostly deals with the questions that are based on either VBODMAS rule or general simplification. If an equation is given with certain mathematical relations, you need to solve them according to the VBODMAS rule.
Tricks:
You should remember the VBODMAS rule thoroughly and first start by solving all the brackets. Sometimes there are various kinds of brackets, so you need to solve them in a particular order that they are implemented on. Most of the cases, ( ) gets solved first.
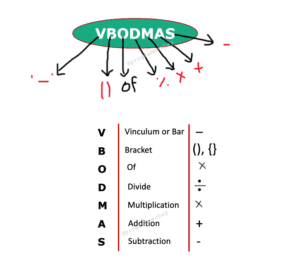
Some Important points :
- From left to right, always multiplication & Division expression must be performed first, and then Addition & Subtraction.
For example,
5*2+3-4/2
first, multiplication and division will be done,
= 10+3-2 i.e ( 5*2 = 10, 4/2 = 2 )
Now, perform addition and subtraction = 11
- Multiplication & Division are of same priorities and Addition & Subtraction are of same priorities
- There can be a situation where multiple types of brackets might exist in the expression to complex it, in order to avoid confusion one should know the order to remove the brackets:
() -> must be solved first,
{} -> then after curly braces
[] -> lastly Rectangular bracket
Simplification Problem Examples
Example: 1035 ÷ [(3/4) of (71+65) – 63/4]
Solution: We will start by solving the brackets first: 1035 ÷ [(3/4) of 136 – 63/4]
Now, we will solve of condition inside the bracket: 1035 ÷ [102 – 63/4]
Solving the bracket we get: 1035 ÷ (345/4)
It’s difficult to solve this, so we will reciprocate the equation inside the bracket and replace ÷ by *
Hence, 1035*(4/345) will give us 12
Example: The price of 10 chairs is equal to that of 4 tables. The price of 15 chairs and 2 tables together is Rs.4000.What will be the total price of 12 chairs and 3 tables?
Solution:
Given that Price ( 10C = 4T ) i.e. 5C = 2T
Now, Price ( 15C + 2T ) = 4000
Using 5C = 2T, we get, 6T + 2T =4000 i.e. T = 500
Hence C=200
Since price of 1 chair is Rs.200 and table is Rs.500.
Therefore, the price of 12 chairs and 3 tables will be Rs.3900.
Example:
(469 + 174)2 – (469 – 174)2 = ?
(469 x 174)
Solution: This type of questions seems to be difficult in first reading but are based on simple tricks. Don’t get hyper after looking into squares of big numbers.
This numerator can be written in the form of (a+b)2 – (a-b)2 = 4ab
Therefore, 4ab/ab = 4
We don’t even need to look at the numbers. Just need to find the pattern and the general mathematical formulae that is used in these equations.
Example: (7 x 7)3 ÷ (49 x 7)3 x (2401)2
Solution: Again, we have big numbers with powers but it seems common that 7 is repeating a lot of times.
So, there is a possibility that 2401 can be equal to some power of 7.
After solving we can see that 2401 is square of 49 which itself is square of 7,
74 = 2401
Therefore we can write the equation as: (7 x 7)3 ÷ (72 x 7)3 x (74)2
(72)3 ÷ (73)3 x (74)2 = 76 ÷ 79 x 78
We know that Xa ÷ Xb = Xa-b and Ya x Yb = Ya+b
Therefore, 76 ÷ 79 x 78 = 76-9+8 = 75
This article is contributed by Shushank Mittal.
